Saccharin – Definition – Saccharin is an artificial sweetener that is 200-700 times sweeter than sugar and approved for use by the FDA. Relevance – Saccharin is not used in cooking or baking due to the presence of a metallic aftertaste; however, it is used in diet foods and beverages.
Saccharomyces (S.) boulardii – Definition – A probiotic (beneficial) yeast used in some dietary supplements. Relevance – Research suggests it may be helpful in preventing and alleviating diarrhea, such as diarrhea from rotavirus in children, diarrhea from small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) in adults, traveler’s diarrhea and antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Salmonella – Definition – Salmonella bacteria are the most frequently reported cause of foodborne illness. Relevance – Salmonella present on raw meat and poultry could survive if the product is not cooked to a safe minimum internal temperature. Salmonella can also cause foodborne illness through cross-contamination, such as when juices from raw meat or poultry come in contact with ready-to-eat foods.
Sarcopenia – Definition -Sarcopenia is the gradual loss of lean muscle mass that occurs naturally with age. Relevance – Sarcopenia can increase the risk of disability, mortality, and severity of co-morbid conditions, but is currently not recognized by the healthcare industry as a disease due to lack of a consensus on diagnosis criteria.
Satiety – Definition – A feeling of fullness after eating, which suppresses the desire to eat again for a period of time. Relevance – Various factors may affect the satiety provided by foods, such as their protein and fiber content.
Saturated fat – Definition – Saturated fat is a type of fat found mostly in animal products like meat and dairy but also tropical oils, such as coconut and palm, that has a strong association with increased cholesterol. Relevance – Raised blood cholesterol resulting from high saturated fat intake can increase risk of heart disease and stroke, so foods high in saturated fat like whole-milk dairy, full-fat cheese, ice cream, butter, meat, and tropical oils should be limited in the diet.
Saw palmetto – Definition –Saw palmetto is a plant, the fruit of which is used medicinally to treat prostate problems. Relevance – Saw palmetto can decrease symptoms of an enlarged prostate and prostate infections; it is also sometimes used to treat colds and upper respiratory infections.
Screen time – Definition – Time spent in front of a screen, such as watching TV, working on a computer, playing video games or using handheld electronic devices. Relevance – Screen time is a sedentary activity, and too much screen time may make it more challenging to control your weight.
Selenium – Definition – Selenium is a trace element found in the diet that acts as an antioxidant and has critical roles in reproduction and thyroid hormone metabolism. Relevance – As an antioxidant, selenium protects against oxidative damage and is most abundant in seafood and organ meats, although it is also found in muscle meats, dairy, cereals and other grains.
Soluble fiber – Definition – Fiber that attracts water and turns to a viscous gel during digestion. It is found in higher amounts in certain foods, such as barley, oats and legumes. Relevance – Soluble fiber may help lower cholesterol and may slow nutrient absorption from the small intestine. That may have the potential to help reduce a person’s blood sugar response after eating.
Sorghum – Definition – Sorghum is a gluten-free grain primarily used for livestock feed. Relevance – Sorghum has gained popularity in U.S. food sources due to the fact that it is a gluten-free grain that can be tolerated by those with Celiac disease or gluten intolerances.
Soy lecithin – Definition – Soy lecithin is a naturally-occuring substance found in soybeans that can act as an emulsifier. Relevance – Soy lecithin is used in processed candy and baked goods, along with many other products, to bind ingredients together.
Spices – Definition – Obtained from root-like stems (rhizomes), flower buds, flower stigmas, fruits (berries), seeds or bark of plants with either woody or non-woody stems. Relevance – Spices are most commonly sold dried (either whole or ground) and have a stronger flavor than herbs.
St. John’s wort – Definition – St. John’s worst is an herb, the flowers and leaves of which are used medicinally to treat some depression symptoms. Relevance – St. John’s wort is used to treat anxiety, fatigue, sleep problems, and appetite loss related to depression; it is also used to treat heart palpitations and some mood disorders.
Statin – Definition – Statins are drugs that are used to lower cholesterol by interfering with the production of cholesterol in the liver. Relevance – Statins are often used when exercise and diet alone do not reduce cholesterol enough. They effectively lower LDL cholesterol levels and raise HDL cholesterol levels, delaying the formation of arterial plaques.
Stearic acid – Definition – A saturated fatty acid (identified chemically as C18:0). It is found in higher amounts in animal fats and cocoa butter (chocolate). Relevance – Stearic acid has a neutral effect on LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. However, as naturally found in foods, stearic acid is often accompanied by other saturated fatty acids associated with increased heart disease risk.
Sterol – Definition – Sterols are compounds found in plants that make up part of the cell membrane; they are similar to cholesterol in structure, but not made in the body. Relevance -Sterols are not well absorbed by the body and have been shown to lower cholesterol absorption in the gut; they have been shown to decrease LDL cholesterol and can be found in plant oils, nuts, legumes, and whole grains.
Streptococcus pneumoniae – Definition – Causes one of the most common types of pneumonia in older adults. Relevance – Preliminary laboratory research suggests vitamin E may help the immune system fight this infection.
Subsidy – Definition – A form of financial aid extended to an economic segment (such as farm businesses or institutions) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Relevance – Some food policy experts are advocating for a fruit and vegetable subsidy to reduce the prices of fruits and vegetables and increase their consumption.
Sucralose – Definition – Sucralose is an artificial sweetener that is 600 times sweeter than sugar and approved for use by the FDA. Relevance -Sucralose is heat stable and therefore can be used on cooking or baking; it is also used as a table sweetener and added to chewing gum, gelatin, and frozen dairy desserts.
Sulforaphane – Definition – Sulforaphane is a compound found in broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables that provides many of the health benefits linked to cruciferous vegetables. Relevance – Some studies suggest that sulforaphane may prevent cancer through epigenetic means, such as increased expression of tumor suppressor proteins.
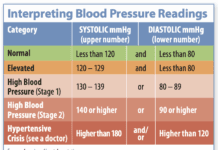
Systolic – Definition – Systolic blood pressure is the top number in a blood pressure reading that is a measure of the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscle contracts (beats). Relevance – Normal systolic blood pressure is below 120 mmHg. Systolic blood pressure of 120-139 indicates pre-hypertension.